- AI, But Simple
- Posts
- GPU Optimization for Machine Learning, Simply Explained
GPU Optimization for Machine Learning, Simply Explained
AI, But Simple Issue #83

Hello from the AI, but simple team! If you enjoy our content, consider supporting us so we can keep doing what we do.
Our newsletter is no longer sustainable to run at no cost, so we’re relying on different measures to cover operational expenses. Thanks again for reading!
GPU Optimization for Machine Learning, Simply Explained
AI, But Simple Issue #83
Machine Learning (ML) revolves around one central operation: matrix multiplication. Depending on the size of these matrices, the computation can be decently fast, but that’s a rare phenomenon in many applications—where matrices can have millions of entries.
Graphical Processing Units (GPUs), originally intended for graphical display and gaming, solve the problem of slow computation with the ability of parallel processing.
Instead of computing repetitive tasks with limited parallelism (although not none), which is the strategy of Central Processing Units (CPUs), GPUs split these tasks into different threads and complete them simultaneously.
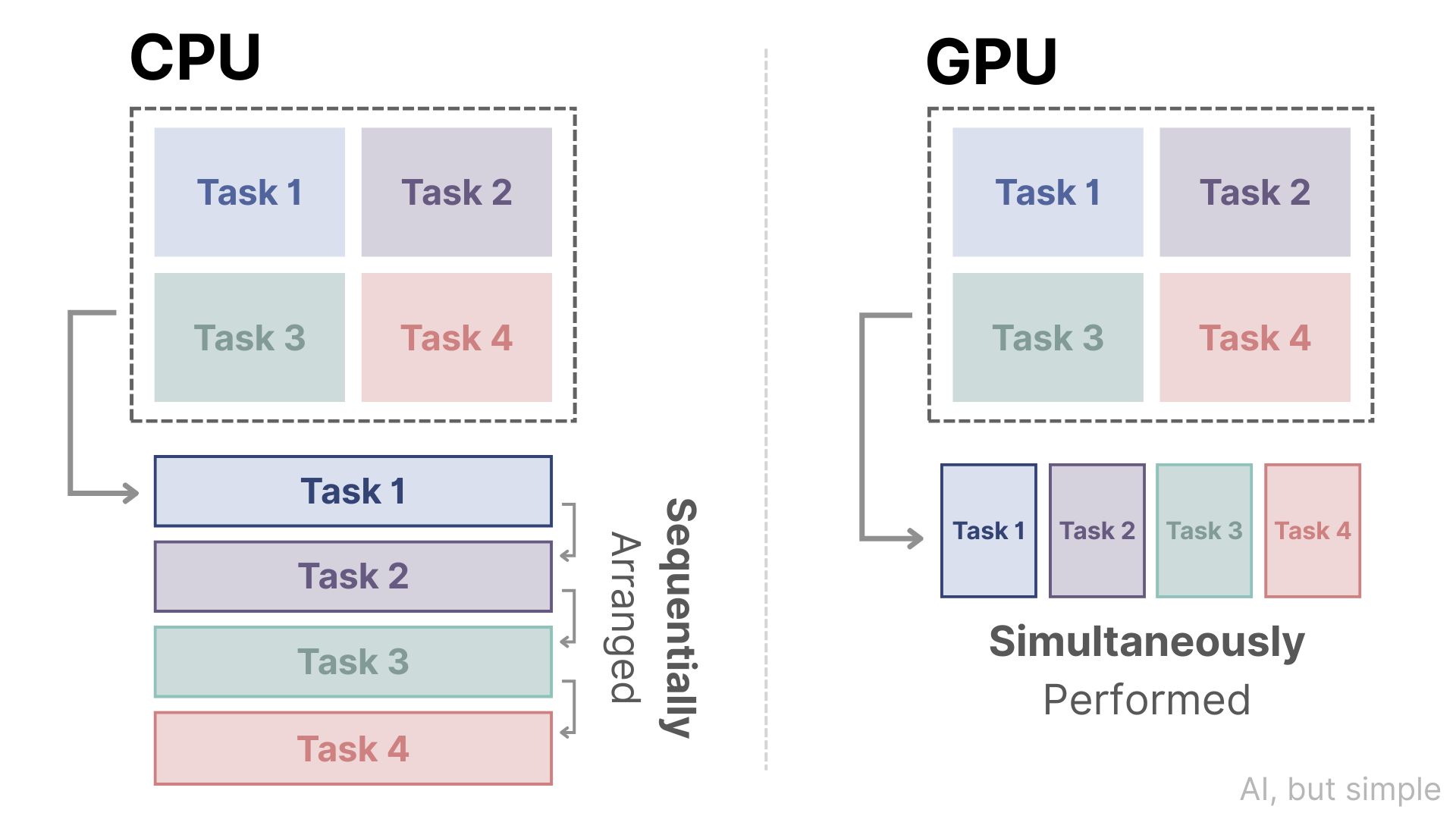
Companies like NVIDIA, AMD, and Intel compete to create more capable GPUs, which are especially in demand due to the field of machine learning, where processing loads of millions of data points is a routine task.
In this issue, we’ll break down:
The infrastructure of a GPU (where its parallel processing comes from)
Methods of optimizing its performance